Urinary marker of oxidative stress in children correlates with molecules in exhaled breath
A. Gisler, K. D. Singh, A. Marten, F. Decrue, U. Frey, P. Sinues and J. Usemann
Real-time breath analysis via secondary electrospray ionization high-resolution mass spectrometry (SESI-HRMS) shows promise as a non-invasive tool for assessing oxidative stress. In a study involving 128 children (25 tobacco smoke-exposed, 103 non-exposed), 71 breath features significantly correlated with urinary levels of the oxidative stress marker 8-iso-prostaglandin F2α (8-iso-PGF2α). Breath analysis moderately predicted urinary 8-iso-PGF2α (concordance correlation: 0.37 ± 0.05), suggesting potential clinical applicability
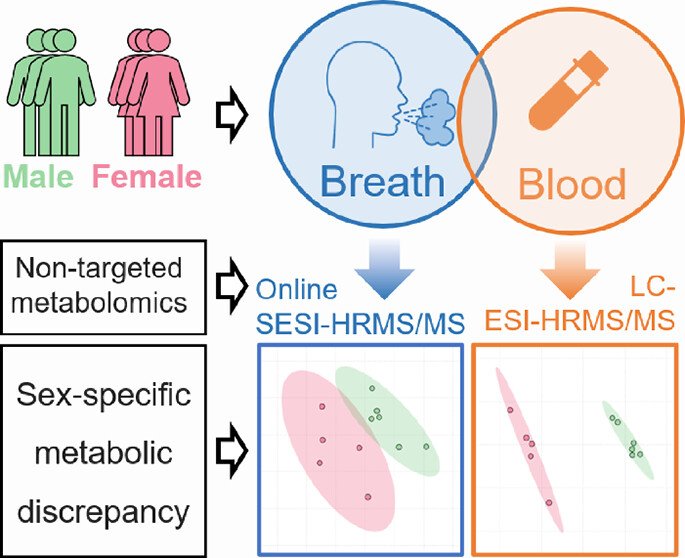
Breath and Blood Metabolomics: A Comparative Study Using SESI-HRMS/MS and UHPLC-ESI-HRMS/MS
Zhifeng Tang, Jianming Yang, Xin Xu, Keda Zhang, Huiling Wang, Xin Luo, Mingliang Fang, Tao Huan, Xue Li
Breath metabolomics enables noninvasive and rapid acquisition of metabolic information by detecting volatile organic compounds (VOCs) in exhaled breath. Secondary electrospray ionization high-resolution tandem mass spectrometry (SESI-HRMS/MS) offers the highest coverage for detecting breath metabolites among current real-time breath analysis techniques. Although it has been generally recognized that metabolites in breath originate from the blood, a molecular-level understanding of the characteristics of metabolites in both breath and blood remains insufficient. In this study, nontargeted analyses of breath and blood samples from 11 healthy volunteers were performed using SESI-HRMS/MS and ultrahigh performance liquid chromatography electrospray ionization high-resolution tandem mass spectrometry (UHPLC-ESI-HRMS/MS), respectively…
Pain induces a rapid characteristic metabolic signature detectable in breath
P. Sinues, M. Richard, K. Singh, D. Sezer, S. Buergler, L. Palermo, Y. Schulz, Z. Tang, X. Luo, U. Frey, P. Cattin, X. Li, J. Gaab
Accurately assessing pain in vulnerable populations—such as children, the elderly, and unconscious patients—remains a critical challenge in healthcare. A new study explores the potential of breath metabolomics as a real-time, objective tool for pain evaluation. Using the cold pressor test (CPT) to induce pain, researchers analyzed exhaled breath with high-resolution mass spectrometry, identifying over 400 metabolic changes within 15 minutes. Key pathways linked to pain signaling, including amino acid metabolism and neurotransmitter activity, showed significant shifts. A neural network classifier effectively distinguished pre- and post-CPT states (AUC=0.856), highlighting the promise of this approach. These findings align with chronic pain research, suggesting a deeper metabolic connection to pain perception. This breakthrough paves the way for observer-independent pain monitoring, with future research needed to tailor insights for personalized pain management strategies.
Rapid detection of Tulipalin A with SESI-Orbitrap MS: an exploration across spring flowers
Kim Arnold, Alejandro Gómez-Mejia, Miguel de Figueiredo, An N. T. Phan, Roy Eerlings, Hendrik G. Mengers & Lars M. Blank
Here, we demonstrated the secondary electrospray ionization coupled Orbitrap mass spectrometry (SESI-Orbitrap MS) methodology for quantifying tulipalin A release from plants upon injury.
Early detection of bacterial pneumonia by characteristic induced odor signatures
Kim Arnold, Alejandro Gómez-Mejia, Miguel de Figueiredo, Julien Boccard, Kapil Dev Singh, Serge Rudaz, Pablo Sinues & Annelies S. Zinkernagel
This study refines the application of the non-invasive Secondary Electrospray Ionization-High Resolution Mass Spectrometry (SESI-HRMS) methodology for real-time and early detection of human respiratory bacterial pathogens in the respiratory tract of a mouse infection model
Molecular breath profile of acute COPD exacerbations
Sarah Basler, Noriane A Sievi, Felix Schmidt, Kai Fricke, Alexandra Arvaji, Jonas Herth, Diego M Baur, Pablo Sinues, Silvia Ulrich and Malcolm Kohler
Metabolic changes in the linoleate, tyrosine, and tryptophan pathways during AECOPD were predominant. Significant metabolic changes occur during COPD exacerbations, predominantly in the linoleate, tyrosine, and tryptophan pathways, which are all linked to inflammation. Real-time exhaled breath analysis enables a good prediction of AECOPD compared to stable state and thus could enhance precision of AECOPD diagnosis and efficacy in clinical practice.
Pharmacometabolomics via real-time breath analysis captures metabotypes of asthmatic children associated with salbutamol responsiveness
Jiafa Zeng, Jakob Usemann, Kapil Dev Singh, Anja Jochmann, Daniel Trachsel, Urs Frey, Pablo Sinues
Pharmacometabolomics via exhaled breath analysis holds promise for patient stratification. Here, we integrate a real-time breath analysis platform in the workflow of an outpatient clinic to provide a detailed metabolic snapshot of patients with asthma undergoing standard clinical evaluations. We observed significant metabolic changes associated with salbutamol inhalation within ∼1 h. Our data supports the hypothesis that sphingolipid metabolism and arginine biosynthesis mediate the bronchodilator effect of salbutamol…
Diagnostic potential of breath analysis – Focus on the dynamics of volatile organic compounds
Wolfram Miekisch, Pritam Sukul, Jochen K. Schubert
As dynamic VOC profiling provides valuable information on kinetics of markers and confounders, it offers huge and so far unexplored potential for physiological, metabolic, therapeutic and environmental monitoring. Driven by new and innovative technologies such as real time mass spectrometry and highly specific sensor systems, future applications may range from home care to ICU monitoring
Ozone Oxidation of the Flame Retardant BDE-209: Kinetics and Molecular-Level Analysis of the Gas-Phase Product Compounds
Siyu Liu, Jinli Xu, Yingxin Xie, Bowen He, Qingxin Deng, Yanan Hu, Jiangping Liu, Davide Vione, Xue Li, Sasho Gligorovski
Real-time measurements of the gas-phase product compounds formed by the reaction of O3 with BDE-209 were performed with a SESI-HRMS in both positive and negative ionization modes…
BreathXplorer: Processing Online Breathomics Data Generated from Direct Analysis Using High-Resolution Mass Spectrometry
Yukai Wang, Zhifeng Tang, Tingting Zhao, Jianming Yang, Wei Zhang, Xue Li, Tao Huan
This work takes a typical real-time HRMS technique as an example, i.e. secondary electrospray ionization high-resolution mass spectrometry (SESI-HRMS), and presents BreathXplorer, an open-source Python package designed for the processing of real-time exhaled breath data comprising multiple exhalations. BreathXplorer is composed of four main modules…
Internal Standard Addition System for Online Breath Analysis
Cedric Wüthrich, Timon Käser, Renato Zenobi, Stamatios Giannoukos
To enable quantitative assessments using SESI-MS, a system was developed to introduce controlled amounts of gases into breath samples and carry out standard addition experiments. The system combines gas standard generation through controlled evaporation, humidification, breath dilution, and standard injection with the help of mass-flow controllers.
Comparative analysis of feature annotation methods for SESI-HRMS in exhaled breath analysis
Cedric Wüthrich,Albin Vadakkechira,Pascal Fuchsmann,Simon Wacker,Renato Zenobi, and Stamatios Giannouko
Secondary electrospray ionization coupled to high-resolution mass spectrometry (SESI-HRMS) is a powerful method for the analysis of exhaled breath in real time. However, feature annotation is challenging due to the flow-injection nature of the technique. To evaluate alternative methods for enhancing feature annotation, a study was conducted where…
Exhaled breath analysis in patients with potentially curative lung cancer undergoing surgery: a longitudinal study
Jonas Herth, Felix Schmidt, Sarah Basler, Noriane A Sievi and Malcolm Kohler
Exhaled breath analysis has emerged as a non-invasive and promising method for early detection of lung cancer, offering a novel approach for diagnosis through the identification of specific biomarkers present in a patient's breath…
Exhalomics as a noninvasive method for assessing rumen fermentationin dairy cows: Can exhaled-breath metabolomics replace rumen sampling?
M. Z. Islam, S. E. Räisänen, A. Schudel, K. Wang, T. He, C. Kunz, Y. Li, X. Ma, A. M. Serviento, Z. Zeng, F. Wahl, R. Zenobi, S. Giannoukos, and M. Niu.
Previously, we used secondary electrospray ionization-mass spectrometry (SESI-MS) to investigate the diurnal patterns and signal intensities of exhaled (EX) volatile fatty acids (VFA) of dairy cows. The current study aimed to validate the potential of an exhalomics approach for evaluating rumen fermentation. The experiment was conducted in a switchback design, with 3 periods of 9 d each, including 7 d for adaptation and 2 d for sampling. Four rumen-cannulated original Swiss Brown (Braunvieh) cows were randomly assigned to 1 of 2 diet sequences (ABA or BAB): (A) low starch (LS; 6.31% starch on a dry matter basis) and (B) high starch (HS; 16.2% starch on a dry matter basis). Feeding was once per day at 0830 h. Exhalome (with the GreenFeed System), and rumen samples were collected 8 times to represent every 3 h of a day, and EX-VFA and ruminal (RM)-VFA were analyzed using SESI-MS and HPLC, respectively. Furthermore, the VFA concentration in the gas phase (HR-VFA) was predicted based on RMVFA and Henry’s Law (HR) constants….
Exhalation metabolomics: A new force in revealing the impact of ozone pollution on respiratory health
Chen Tao, Peter Mettke, Yaru Wang, Xue Li, Ligang Hu
Highlights
Near-surface ozone pollution has a significant impact on respiratory health.
Lung microenvironment is involved in respiratory health effects of ozone pollution.
Exhalation metabolomics provides a new method to explore the respiratory health effects of ozone pollution.
Exhalation metabolomics could be a potential basis for concentration limits in ozone pollution control.
Metabolic trajectories of diabetic ketoacidosis onset described by breath analysis
Mo Awchi, Kapil Dev Singh, Sara Bachmann Brenner, Marie-Anne Burckhardt, Melanie Hess, Jiafa Zeng, Alexandre N Datta, Urs Frey, Urs Zumsteg, Gabor Szinnai, Pablo Sinues
Purpose: This feasibility study aimed to investigate the use of exhaled breath analysis to capture and quantify relative changes of metabolites during resolution of acute diabetic ketoacidosis under insulin and rehydration therapy…
Alternative electrolyte solutions for untargeted breath metabolomics using secondary-electrospray ionization high-resolution mass spectrometry
Cedric Wüthrich, Renato Zenobi, Stamatios Giannoukos
Rationale
Secondary-electrospray ionization (SESI) coupled with high-resolution mass spectrometry is a powerful tool for the discovery of biomarkers in exhaled breath. A primary electrospray consisting of aqueous formic acid (FA) is currently used to charge the volatile organic compounds in breath. To investigate whether alternate electrospray compositions could enable different metabolite coverage and sensitivities, the electrospray dopants NaI and AgNO3 were tested….
Data Collection of" Alternative Electrolyte Solutions for Untargeted Breath Metabolomics with Secondary-Electrospray Ionization High-Resolution Mass Spectrometry"
Cedric Wüthrich, Renato Zenobi, Stamatios Giannoukos
The mass spectrometer used in this study was an Orbitrap Q-Exactive Plus (Thermo Scientific) operated with the manufacturer’s standard control software (ExactiveTune, version 2.9, Thermo Scientific) and Xcalibur (version 4.1. 31.9, Thermo Scientific). Mass calibration was done according to the instrument manual and was always more recent than seven days according to specifications…
Real-time Analysis of Organic Composition of Oral and Nasal Breath Air by High Resolution Mass Spectrometry
WANG Kangyi, TAO Chen, LUO Zuo, TANG Zhifeng, BAI Te, LI Hang, HU Ligang, ZHANG Zuo, LI Xue
Breath samples can be collected from the oral and nasal cavity.However,the oral and nasal environment affect the chemical composition of breath sample. It was found that the number of unique component(m/z)detected in mouth-exhaled breath(167)was 2.2 times greater than that detected in nose-exhaled breath(76), which might result from the complex environment in oral cavity. The signal intensity of common component (163) was significantly different between mouth-exhaled breath and nose-exhaled breath. Additionally, the elemental composition analysis showed that the proportion of polar compounds detected in nose-exhaled breath was higher than that in mouth-exhaled breath. This study demonstrated that there was significant differences in the chemical composition between mouth-exhaled and nose-exhaled breath, which provided a theoretical basis for selection of exhalation mode.
Advances in secondary electrospray ionization for breath analysis and volatilomics
Stamatios Giannoukos, Cedric Wüthrich
This review discusses the technical aspects behind SESI, the advancements, and the technical hurdles faced. Additionally, the recent advances in the applications of SESI in human and animal-centered research are presented.